Investigating fairness and bias in E2E SLU Models
Published:
Status: Available ✅
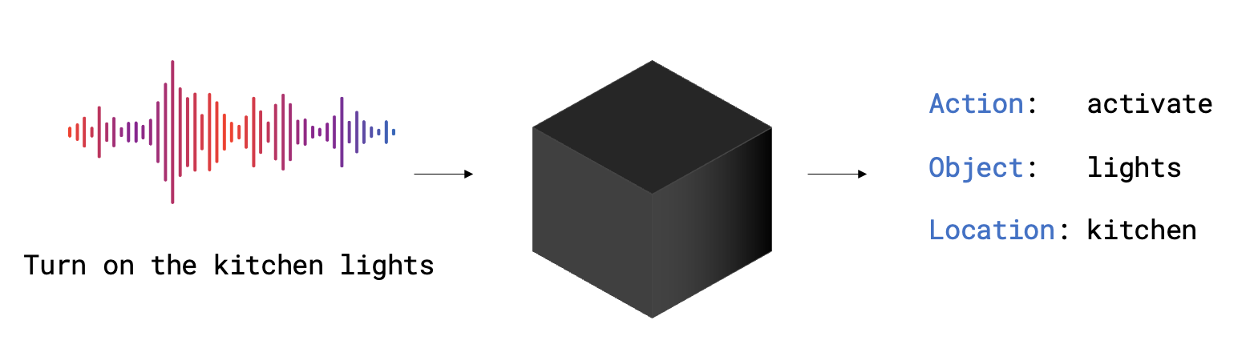
Spoken language understanding (SLU) systems typically rely on automatic spee h recognition (ASR) and natural language understanding (NLU) models to derive meaning from speech signals and text. However, end-to-end (E2E) models offer a direct approach to extracting semantic information from speech signals, leading to improved accuracy and reduced complexity. Nonetheless, E2E models are complex black-box processes, making it difficult to explain their predictions and interpret their results. Therefore, investigating problematic data subgroups is crucial for understanding and debugging AI pipelines to ensure model fairness.
This project is in collaboration with Amazon Alexa AI.
The main objectives of this thesis are:
- Analyze the state-of-the-art E2E SLU models.
- Identify models’ bias and source of errors in different scenarios (incremental and curriculum learning).
- Demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach across different models, datasets, tasks.
- (Optional) Propose a novel approach to mitigate the bias and improve the model’s performance.
References:

